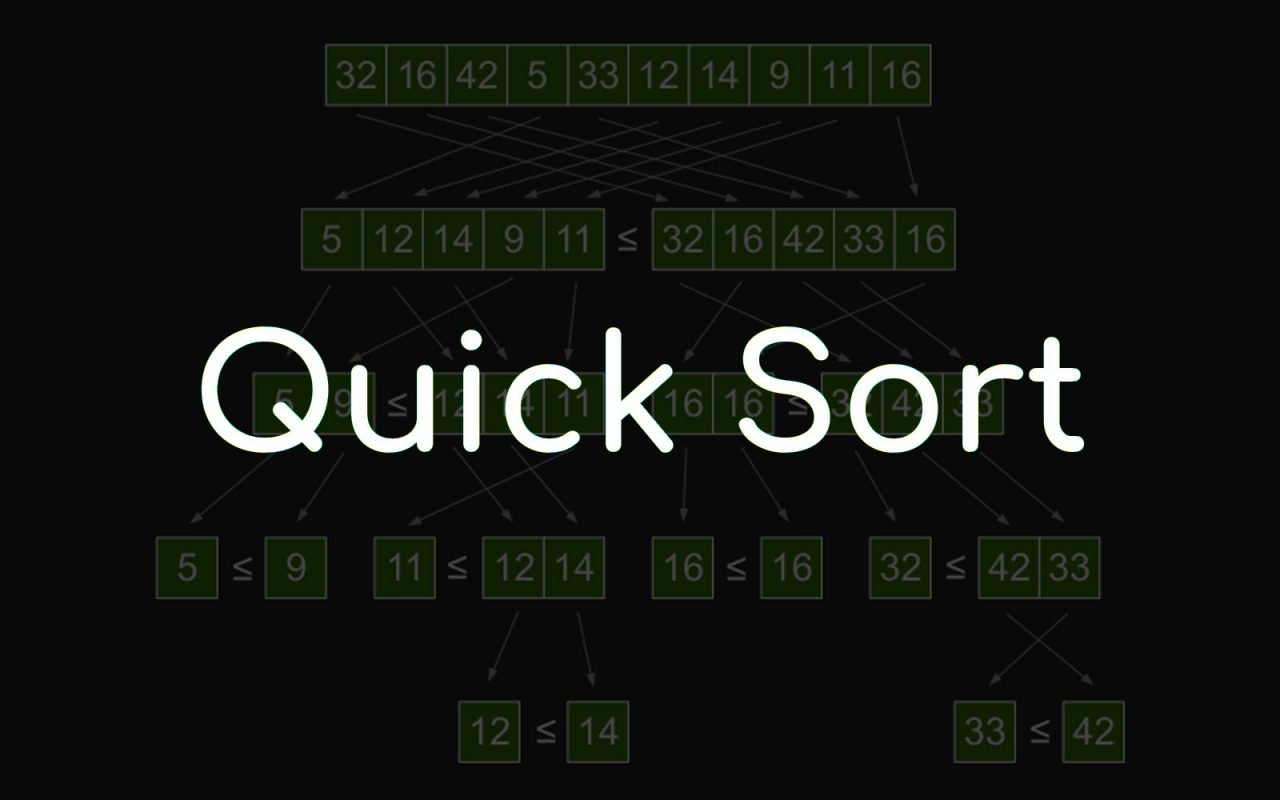
Thuật toán sắp xếp nhanh QuickSort hoạt động như thế nào?
Cách lựa chọn Pivot trong thuật toán sắp xếp nhanh:
Trong một mảng, dãy số cho trước, chúng ta có thể lựa chọn pivot bằng các cách sau:
- Luôn Chọn Phần từ đầu tiên của mảng
- Luôn chọn phần tử cuối cùng của mảng
- Chọn 1 phần tử random trong mảng
- Chọn phần tử có giá trị nằm giữa mảng (median element)
Thuật toán phân đoạn partition trong quick sort ( thuật toán sắp xếp nhanh):
Quan trọng chính của thuật toán sắp xếp quick sort là việc phân đoạn dãy số (Xem hàm partition()). Công việc chính của việc phân đoạn là:
- Cho một mảng và xác định phần tử X là pivot
- Đặt X vào đúng vị trí của mảng đã sắp xếp
- Di chuyển tất cả các phần tử của mảng nhỏ hơn X qua bên trai, và lớn hơn sang bên phải
Khi đó ta sẽ có 2 mảng con: mảng bên trai của X và mảng bên phải của X. Tiếp tục công việc với mỗi mảng con(chọn pivot, phân đoạn) cho tới khi mảng được sắp xếp.
Hướng dẫn code phân đoạn partition:
- Đặt pivot là phần tử cuối cùng của dãy số arr.
- Chúng ta bắt đầu từ phần tử trái nhất của dãy số có chỉ số là left, và phần tử phải nhất của dãy số có chỉ số là right -1(bỏ qua phần tử pivot).
- Chừng nào left < right mà arr[left] > pivot và arr[right] < pivot thì đổi chỗ hai phần tử left và right.
- Sau cùng, ta đổi chỗ hai phần tử left và pivot cho nhau. Khi đó, phần tử left đã đứng đúng vị trí và chia dãy số làm đôi(bên trái và bên phải).
Ví dụ thuật toán phân đoạn :
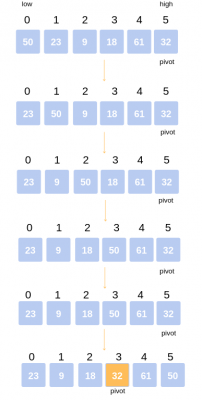
Trong ví dụ sau đây, chúng ta có mảng 6 số: 50, 23, 9, 18, 61, 32.
Chọn pivot là số cuối cùng có giá trị 32.
So sánh số bên trái đầu tiên là 50 > 23(số bên phải) và 50 > 32 (pivot). => Đổi vị trí 50 với 23.
So sánh tiếp tục 50 > 9 (số bên phải) và 50 > 32 (pivot) => Đổi vị trí 50 với 9
So sánh tiếp tục 50 > 18 (số bên phải) và 50 > 32 (pivot) => Đổi vị trí 50 với 18
So sánh tiếp tục 50 < 61 (số bên phải) và 50 > 32 (pivot) => Giữ nguyên vị trí 50
So sánh tiếp tục 50 < 32 (số bên phải) và 50 > 32 (pivot) => Đổi ví trí 50 với 32.
Vậy sau bước này chúng ta có 2 mảng lớn hơn 32 và nhỏ hơn 32. Tiếp tục làm lại như vậy với 2 mảng.
Code minh họa phân đoạn:
int partition (int arr[], int low, int high)
{
int pivot = arr[high]; // pivot
int left = low;
int right = high - 1;
while(true){
while(left <= right && arr[left] < pivot) left++; // Tìm phần tử >= arr[pivot]
while(right >= left && arr[right] > pivot) right--; // Tìm phần tử <= arr[pivot] if (left >= right) break; // Đã duyệt xong thì thoát vòng lặp
swap(&arr[left], &arr[right]); // Nếu chưa xong, đổi chỗ.
left++; // Vì left hiện tại đã xét, nên cần tăng
right--; // Vì right hiện tại đã xét, nên cần giảm
}
swap(&arr[left], &arr[high]);
return left; // Trả về chỉ số sẽ dùng để chia đổi mảng
}
Code minh họa phân quickshort:
void quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high)
{
if (low < high)
{
/* pi là chỉ số nơi phần tử này đã đứng đúng vị trí
và là phần tử chia mảng làm 2 mảng con trái & phải */
int pi = partition(arr, low, high);
// Gọi đệ quy sắp xếp 2 mảng con trái và phải
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1);
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
Hướng dẫn code thuật toán quicksort:
Hướng dẫn code thuật toán quicksort bằng C , C++, Java và Python
Implementation of Quick Sort Algorithm in C:
# include <stdio.h>
// to swap two numbers
void swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
int partition (int arr[], int low, int high)
{
int pivot = arr[high]; // selecting last element as pivot
int i = (low - 1); // index of smaller element
for (int j = low; j <= high- 1; j++)
{
// If the current element is smaller than or equal to pivot
if (arr[j] <= pivot)
{
i++; // increment index of smaller element
swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);
}
}
swap(&arr[i + 1], &arr[high]);
return (i + 1);
}
/*
a[] is the array, p is starting index, that is 0,
and r is the last index of array.
*/
void quicksort(int a[], int p, int r)
{
if(p < r)
{
int q;
q = partition(a, p, r);
quicksort(a, p, q-1);
quicksort(a, q+1, r);
}
}
// function to print the array
void printArray(int a[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i=0; i < size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {9, 7, 5, 11, 12, 2, 14, 3, 10, 6};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
// call quickSort function
quicksort(arr, 0, n-1);
printf("Sorted array: \n");
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Quicksort example program in c++:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
// Swapping two values.
void swap(int *a, int *b)
{
int temp;
temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
// Partitioning the array on the basis of values at high as pivot value.
int Partition(int a[], int low, int high)
{
int pivot, index, i;
index = low;
pivot = high;
// Getting index of the pivot.
for(i=low; i < high; i++)
{
if(a[i] < a[pivot])
{
swap(&a[i], &a[index]);
index++;
}
}
// Swapping value at high and at the index obtained.
swap(&a[pivot], &a[index]);
return index;
}
// Random selection of pivot.
int RandomPivotPartition(int a[], int low, int high)
{
int pvt, n, temp;
n = rand();
// Randomizing the pivot value in the given subpart of array.
pvt = low + n%(high-low+1);
// Swapping pivot value from high, so pivot value will be taken as a pivot while partitioning.
swap(&a[high], &a[pvt]);
return Partition(a, low, high);
}
int QuickSort(int a[], int low, int high)
{
int pindex;
if(low < high)
{
// Partitioning array using randomized pivot.
pindex = RandomPivotPartition(a, low, high);
// Recursively implementing QuickSort.
QuickSort(a, low, pindex-1);
QuickSort(a, pindex+1, high);
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int n, i;
cout<<"\nEnter the number of data elements to be sorted: ";
cin>>n;
int arr[n];
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<"Enter element "<<i+1<<": ";
cin>>arr[i];
}
QuickSort(arr, 0, n-1);
// Printing the sorted data.
cout<<"\nSorted Data ";
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout<<"->"<<arr[i];
return 0;
}
// Java program for implementation of QuickSort
class QuickSort
{
/* This function takes last element as pivot,
places the pivot element at its correct
position in sorted array, and places all
smaller (smaller than pivot) to left of
pivot and all greater elements to right
of pivot */
int partition(int arr[], int low, int high)
{
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = (low-1); // index of smaller element
for (int j=low; j<high; j++)
{
// If current element is smaller than or
// equal to pivot
if (arr[j] <= pivot)
{
i++;
// swap arr[i] and arr[j]
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
// swap arr[i+1] and arr[high] (or pivot)
int temp = arr[i+1];
arr[i+1] = arr[high];
arr[high] = temp;
return i+1;
}
/* The main function that implements QuickSort()
arr[] --> Array to be sorted,
low --> Starting index,
high --> Ending index */
void sort(int arr[], int low, int high)
{
if (low < high)
{
/* pi is partitioning index, arr[pi] is
now at right place */
int pi = partition(arr, low, high);
// Recursively sort elements before
// partition and after partition
sort(arr, low, pi-1);
sort(arr, pi+1, high);
}
}
/* A utility function to print array of size n */
static void printArray(int arr[])
{
int n = arr.length;
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i)
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
System.out.println();
}
// Driver program
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = {10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5};
int n = arr.length;
QuickSort ob = new QuickSort();
ob.sort(arr, 0, n-1);
System.out.println("sorted array");
printArray(arr);
}
}
# Python program for Quicksort
# This function takes last element as pivot, places
# the pivot element at its correct position in sorted
# array, and places all smaller (smaller than pivot)
# to left of pivot and all greater elements to right
# of pivot
def partition(arr,low,high):
i = ( low-1 ) # index of smaller element
pivot = arr[high] # pivot
for j in range(low , high):
# If current element is smaller than or
# equal to pivot
if arr[j] <= pivot:
# increment index of smaller element
i = i+1
arr[i],arr[j] = arr[j],arr[i]
arr[i+1],arr[high] = arr[high],arr[i+1]
return ( i+1 )
# The main function that implements QuickSort
# arr[] --> Array to be sorted,
# low --> Starting index,
# high --> Ending index
# Function to do Quick sort
def quickSort(arr,low,high):
if low < high:
# pi is partitioning index, arr[p] is now
# at right place
pi = partition(arr,low,high)
# Separately sort elements before
# partition and after partition
quickSort(arr, low, pi-1)
quickSort(arr, pi+1, high)
# Driver code to test above
arr = [10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5]
n = len(arr)
quickSort(arr,0,n-1)
print ("Sorted array is:")
for i in range(n):
print ("%d" %arr[i]),
Trên đây là giới thiệu thuật toán quick sort là gì?, và cách lập trình và app dụng thuật toán quick sort.